Vascular Bundle In Monocot Leaf. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Vascular bundles vary in their size. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. Water containing cavity is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present.
Vascular Bundle In Monocot Leaf . Bundle Sheaths Also Surround The Vascular Bundles In Monocot Stems.
Pdf Parallel Venation And Transport Of Water In Monocot Leaves. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Water containing cavity is present. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of.
Dicot plants leaves have a reticulate venation system.
The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Monocot leaves have large vascular bundles in them, but dicot leaves have both the small and large vascular bundles in them. Vascular bundles arranged in concentric circles in dicot stem. The plant vascular system the vascular system of contemporary seed plants is composed of a coherent and continuous network of strands called vascular bundles (esau, 1965a). Their vascular bundles are scattered. The transport itself happens in vascular tissue, which exists in two forms: The main difference between stems of both the plants is due to the arrangement of the vascular bundle. A bundle sheath surrounds each vascular bundle, or vein, in monocot and dicot leaves. These examples reflect their shared ancestry. Monocot leaves are isobilateral i.e., both surfaces look the same and are structurally the same and are both exposed to the sun (usually vertically oriented). So they are called collateral and conjoint. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Monocots have a single cotyledon and long and narrow leaves with parallel veins. Describe the difference in the arrangement of vascular bundles in the monocot and dicot stems. Conjoint vascular bundles are seen in stem and leaves. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Label the parts of a monocot young stem section: Typical vascular bundles are conjoint vascular bundles. In the vascular bundles of dicot leaves, xylem and phloem are present on same radius and also present side by side. Closeup of vascular bundles (indicated by arrow) surrounded by cortical tissue. Three types of conjoint vascular bundles are seen, they are: The parallel venation in monocot leaves is reflected in the near similar sizes of vascular bundles (except in main veins) as seen in vertical sections of the leaves. in this figure the difference of vascular bundle in the monocot and dicot. The ground tissue is the tissue neither vascular nor dermal tissue in the monocot. Dicots have two cotyledons and broad leaves with network of veins. List the basic functions of stems. Epidermis, cortex, vascular bundles, xylem, phloem do ds @ 9 8 os 92 @ @ 09 20.02. Peripheral to the endodermis is the cortex, and peripheral to that is the epidermis. …organized into discrete strands called vascular bundles, each containing xylem and phloem. Name the region on a stem where a leaf arises. The bundles are surrounded by large parenchyma in the cortex region.
Plant Microscope Exercise Biology4friends - It Has Close Vascular Bundles
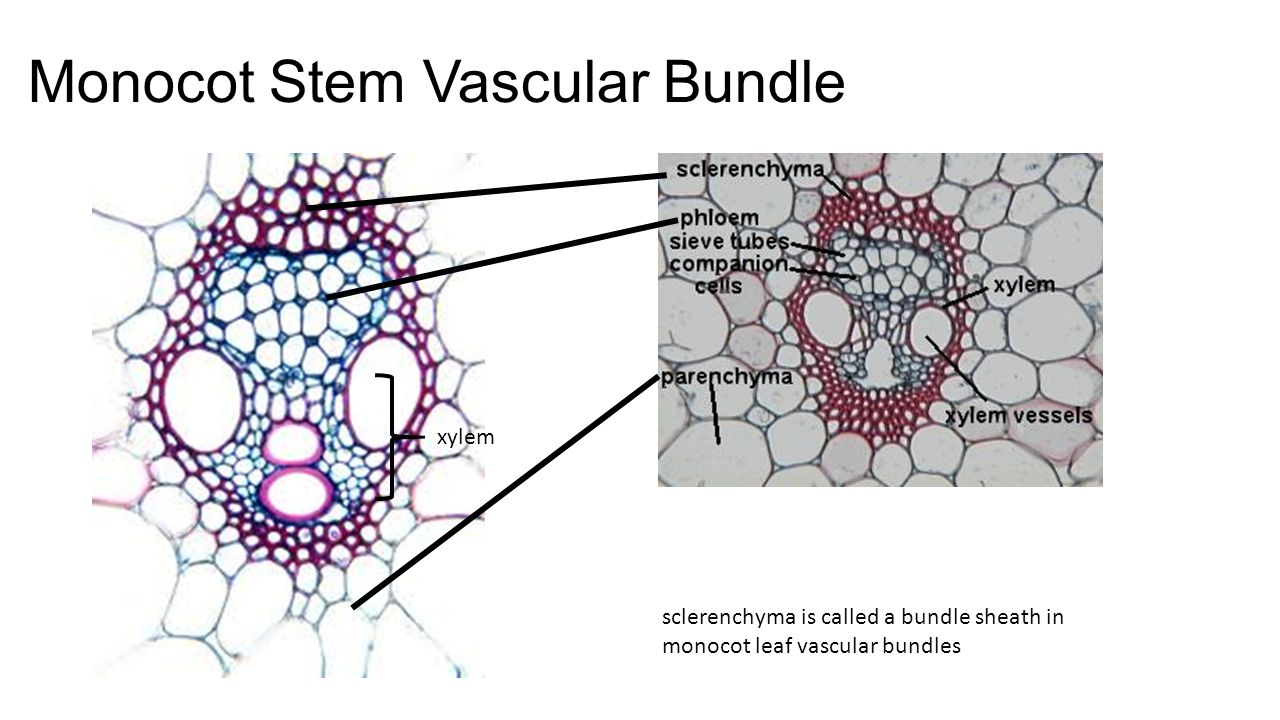
Monocot Stem Vascular Bundle In Zea Microscope Art Vascular Image. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Water containing cavity is present. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Vascular bundles vary in their size. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma.
What Is The Indifference Between A Dicot And Monocot Leaf Quora , Scattered Vascular Bundles In Monocot Stem.
Plant Tissues And Organs Biology For Majors Ii. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Water containing cavity is present. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides.
Leaves Ho F18 Pdf Monocot Leaf Vascular Bundle Cuticle Epidermis Trichromes Spongeymesophyll Epidermis Cuticle Trichomes Vb Phloem Zylem Guard Opening Course Hero : Internode is the distance between two adjacent nodes of the stem.
The Diagram Given Below Represents The T S Of Monocot Leaf Identify The Parts Labelled As A B C And D Which Denote Their Functions And Choose The Correct One Given Below. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Water containing cavity is present. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present.
What Is The Difference Between A Dicot And A Monocot Stem Quora , It Consists Of Tightly Arranged Parenchyma Cells In Dicots And Sclerenchyma Cells In Monocots.
Subfamily Conostylidoideae Leaf Cross Sections A B Anigozanthos Download Scientific Diagram. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Vascular bundles vary in their size. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Water containing cavity is present. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly.
Difference Between Dicot And Monocot Leaf With Comparison Chart Biology Reader : Vascular Bundles Are Collateral And Closed.
Understanding The Difference Between Monocot And Dicot Stem Viva Differences. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Vascular bundles vary in their size. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. Water containing cavity is present. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of.
Monocot Leaf Vs Dicot Leaf 16 Basic Differences With Comparison Table Viva Differences : It Has Vascular Cambium E.
Stem Overview. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Vascular bundles vary in their size. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Water containing cavity is present. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present.
Monocot Vs Dicot Difference And Comparison Diffen : Stomata On Both The Surfaces.
Plant Anatomy Biology4isc. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Water containing cavity is present. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues.
Plant Shoot System : Dicot Plants Leaves Have A Reticulate Venation System.
Exe. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of. Water containing cavity is present. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue.
Stems , Monocot Leaves Have Large Vascular Bundles In Them, But Dicot Leaves Have Both The Small And Large Vascular Bundles In Them.
13 2 Monocot Leaves Biology Libretexts. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Vascular bundles vary in their size. Water containing cavity is present. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of.
What Is The Indifference Between A Dicot And Monocot Leaf Quora . Each Vascular Bundle Is Encircled By Bundle Sheath Made Up Of Sclerenchyma.
Plant Anatomy Biology4isc. The vascular bundle is large in dorsiventral leaf, and in monocot leaf, both large and small vascular bundle is present. Difference # vascular bundle of monocot stem: Bundle sheath is developed either partly or completely surrounding the vascular bundle. Each vascular bundle is encircled by bundle sheath made up of sclerenchyma. They are of different sizes, the smaller being restricted to peripheral sides. The vascular bundles are scattered in the ground tissue. Each vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral and closed. Vascular bundles are scattered in ground tissues. Vascular bundles vary in their size. In a dicot leaf stomata are usually present on the lower surface of the leaf, a condition referred to as hypostomatic. They appear to be embedded in ground tissue. Many vascular bundles are arranged parallaly. The vascular bundle is large in dicot leaf whereas in monocot leaf, both small and large vascular bundles are present. Water containing cavity is present. Another feature is that in dicot leaf the intercellular space is more due to the presence of air cavities whereas, in monocot, the intercellular space is small as they lack air cavities and due to the compact arrangement of.